Why Do People Say Bad Things About The Capitalist System That Delivers Superabundance?
Consider this chart. It appears in a book entitled A Farewell To Arms: A Brief Economic History Of The World and illustrates the worldwide change in personal income over 3000 years.
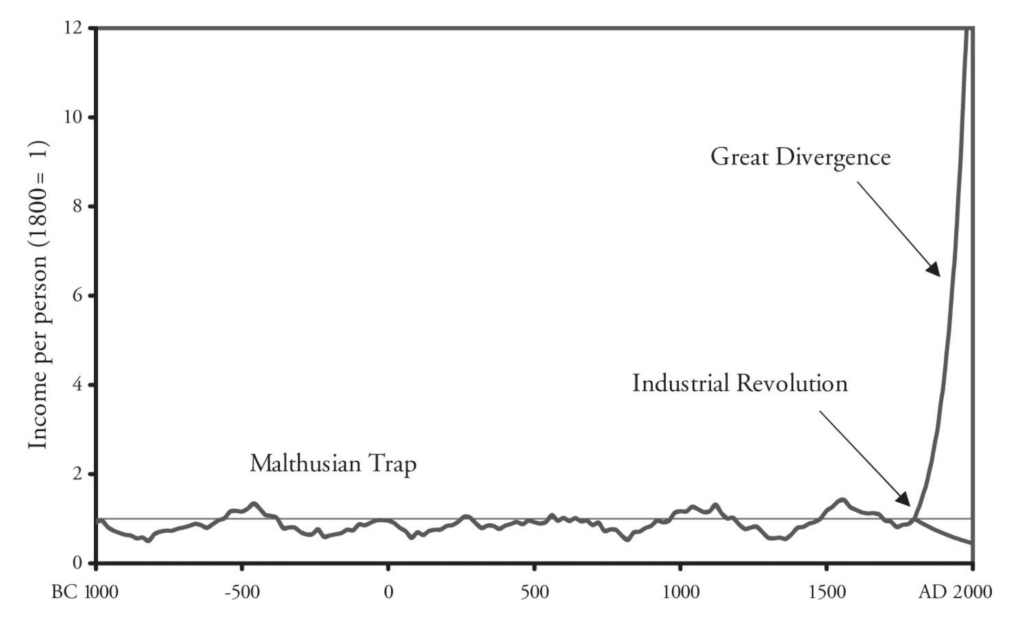
We can think of increased personal income per person as pleasurable progress for all. Increased income is a proxy for many life improvements: better food and beverages, better shelter from heat and cold, better health and better healthcare, better education, better jobs, better transportation, better entertainment, expanded knowledge, greater freedom, and many more in a long list that covers all of life.
As the chart shows, the progress is recent. There was no progress in income per person for the first 2800 years or so depicted in this chart, and then a high energy surge of almost exponential growth in the most recent 200 years. The pivot point is the invention and introduction of capitalism.
The pivot is often labeled “the Industrial Revolution” (as it is in our chart), referring to new forms of physical capital such as steam engines and factories that proved capable of producing more and better goods at lower and lower prices and creating the jobs that paid the wages that increased income per person and gave individuals the opportunity to become consumers. It was a technological revolution, a knowledge revolution, and, most importantly, an economic system revolution, the switch to capitalism.
Over the 200 years since the switch, capitalism has delivered more than personal income growth; it has delivered superabundance. That’s the term employed by researchers Marian Tupy and Gaye Pooley in their book of that title. Superabundance is defined by the phenomenon of us each needing to spend less and less time working to purchase more and more goods and services. It’s a new economics, not of scarcity but of abundance.
A similar story is told by Hans Rosling and Anna Rosling Rönnlund in their 2018 book, Factfulness. They provide us with long lists of “good things that are getting better, and bad things that are decreasing”. The former list includes child cancer survival, access to education, women’s rights, clean water, literacy and democracy. The latter list includes child labor, hunger, smallpox, oil spills, and many more.
These and many similar books and papers provide extensive data compilations regarding the improved lives we all enjoy as a result of capitalism. So why do so many people – students, intellectuals, democratic politicians, writers, celebrities, and cultural influencers in general – speak so badly of capitalism?
The authors of the books we’ve quoted put it down to human psychology, that we are wired to be apprehensive, skeptical, and negative even in the face of incontrovertible evidence to the contrary. Our negative affect comes from our time roaming around prehistoric forests in constant fear of being attacked by some predator. The Roslings point to psychology research that indicates that humans have a gap instinct. We are prone to divide the world in two (e.g. developed economies versus underdeveloped economies, or rich versus poor) and focus on the gap between the two extremes of perception we have just created. We don’t see a continuum and we don’t see continued progress for everyone.
It’s a little hard to accept this psychological perspective in the 21st Century, when there is so much data to refute it, but if we are looking to psychology for an explanation, we can certainly look at envy. According to Helmut Schoeck (in Envy: A Theory Of Social Behavior), envy is universal among humans.
Envy is a drive which lies at the core of man’s life as a social being, and which occurs as soon as two individuals become capable of mutual comparison.
From a perspective of envy, the absolute gains that capitalism brings are ignored and the perception that some gain more than others prevails. Envy itself is an individual emotion – a lonely one since it’s a rejection of relationships – but the great danger occurs when a culture of envy is cultivated. That’s exactly what happens in our educational institutions, both universities and high schools and even elementary and middle schools. A class of educators, resentful because they feel underpaid and underappreciated in the capitalist system that rewards innovative value-creating entrepreneurship more highly than institutional maintenance, teach our children that capitalism is unfair, extractive, and exploitative.
The teachers are reinforced by the communicators in the media, the writers, influencers, and talking heads who find that anti-capitalist content is amenable to their customers who have passed through the channels of education and become permanently misguided by the perspective they absorbed there. The media continuously reinforce the disaffected envy of their audience, deepening it, extending it, and distorting reality even further. The negativity instinct in the media leads to selective reporting and downright distortion of facts.
And then the politicians and government bureaucrats pile on. Politicians have no interest in progress and improvement. Their stock in trade is to point out how the opposition is failing – undermining or destroying prosperity. They also feed on the idea of the gap – that their constituency suffers by comparison to whomever the politicians decide to compare them to: women to men, non-whites to whites, Southerners to Northerners, less-educated to more-educated, my constituents to your constituents. It’s always about the gap for politicians. And the notion of the gap leads them to anti-capitalist rhetoric: capitalism is responsible for these gaps, that wouldn’t otherwise occur. There’d be equality under alternative systems.
Government bureaucrats can claim to fix the gap problem in a different system that they run. Call it socialism, call it public-private, call it interventionism or regulationism, call it the entrepreneurial state. Governments are anti-capitalist because capitalism gives no role to government. Government can divide the pie, but only after capitalism has created the recipe for the pie, assembled the pie ingredients, baked the pie, served the pie, accepted and incorporated the feedback of the consumers of the pie, and nurtured the broad and deep market for pies that generates the commercial revenues that governments can then tax and redistribute. Politicians and bureaucrats must condemn capitalism so that they can offer their so-called solutions to the problems they claim capitalism causes.
We have a deep and wide circle of groups willing to say bad things about capitalism: educators, intellectuals; the students and others whom they influence; the media who act as their cheerleaders; and politicians and bureaucrats whose professional incentives are to undermine the popularity of capitalism in order to justify their own anti-capitalist ends and means. Together, they represent a formidable array.
There isn’t a word for fans of capitalism. If we use the word “capitalist”, it’s perceived as derogatory. Whatever the name for fans of capitalism, we need them to be confident, vocal, well-armed with data, and positive and persuasive in its presentation. We need to strengthen the pro-capitalist mentality.