The Value Creators Podcast Episode #34. David Kong’s Entrepreneurial Voyage from Finance to Fine Glassware
David Kong discusses his transition from Finance to Entrepreneurship and the process of building a supply chain for a product with exclusive features, such as thin, and handcrafted glasses. He explains how he searched for manufacturers, tested samples, and addressed production issues. Despite challenges with finding warehouses and improving packaging, Kong emphasizes the importance of creating value for customers. He shares insights on the emotional value of Glasvin stemware, its impact on the drinking experience, and the evolution of consumer preferences in the wine industry. Additionally, Kong discusses his direct-to-consumer (DTC) model, marketing strategies, and the significance of inbound sales for Glasvin.
Throughout the conversation, Kong underscores the value of efficient operations, strategic partnerships, and customer-centric approaches in building and scaling a successful business like Glasvin.
Resources:
Database and Analytics company: SOMM.AI
Glasvin (Manufacturing company)
David Kong on LinkedIn
Shownotes:
0:00 | Intro: Origin Story and Entrepreneurial Mindset
02:12 | Origin Story and Entrepreneurial Mindset
05:05 | Idea of Somm.AI Came From Experience
06:19 | How Did Personal Interest Evolve into a Business?
09:18 | Value Proposition for B2B Users: Benefits and Analytics
10:47 | Big Claim: Largest Updated or Updating Database of its Kind
12:49 | Attracting High-Price Point Luxury Wines
13:43 | Global Database
14:28 | Glasvin: Origin Story
19:07 | Building a Supply Chain
23:03 | What’s The Emotional Value of Glasvin?
25:36 | Evolution of Desired Experiences is Fascinating
27:26 | How Did Packaging Evolve
29:25 | Direct-To-Consumer Model
30:44 | B2B Business: Selling to Business Customers
34:45 | Conferences: Getting in Touch with Restaurants
37:53 | Wrap-Up
Knowledge Capsule
Origin of Somm.AI (Wine List Aggregator):
- Initially conceived as a personal tool to find rare wines.
- Evolved into a software business after experiencing success with user engagement.
- Adapted business model from B2C to B2B due to changing market conditions and opportunities.
Value Proposition for B2B Users:
- Offers benchmarking capabilities for restaurants to assess performance and competition.
- Provides analytics and insights to identify trends and target opportunities in the market.
Market Dynamics and Competition:
- David Kong shares that Somm.Ai targets on-premise wine data, serving a niche yet valuable segment.
- Faces competition from established players like Nielsen but focuses on unique data sets and pricing strategies.
- Recognizes challenges in entering the market due to technical complexities and limited entrepreneurial interest.
Global Reach and Expansion:
- Capable of expanding database globally based on client demand.
- Acknowledges regional variations in wine list availability and penetration rates.
Transition to Glasvin (Glassware Business):
- Explored entrepreneurship opportunities beyond software due to the time-to-revenue constraints.
- David shares how he identified the market gap in affordable, high-quality wine glasses and opted to start his own brand, leveraging importing experience and existing demand.
Challenges and Opportunities in E-commerce:
- David Kong recognized e-commerce as a viable business model with the potential for success.
- Found opportunities to offer quality products at competitive prices.
- Successfully launched Glasvin as an e-commerce venture in 2020, capitalizing on market demand and personal interest in wine accessories.
Product Development and Supply Chain:
- David reached out to multiple manufacturers via email to find one willing to produce the desired glasses.
- The process involved requesting samples, evaluating quality, and addressing production issues.
- David shares the initial challenges included finding manufacturers capable of meeting specific criteria, such as glass thickness and weight.
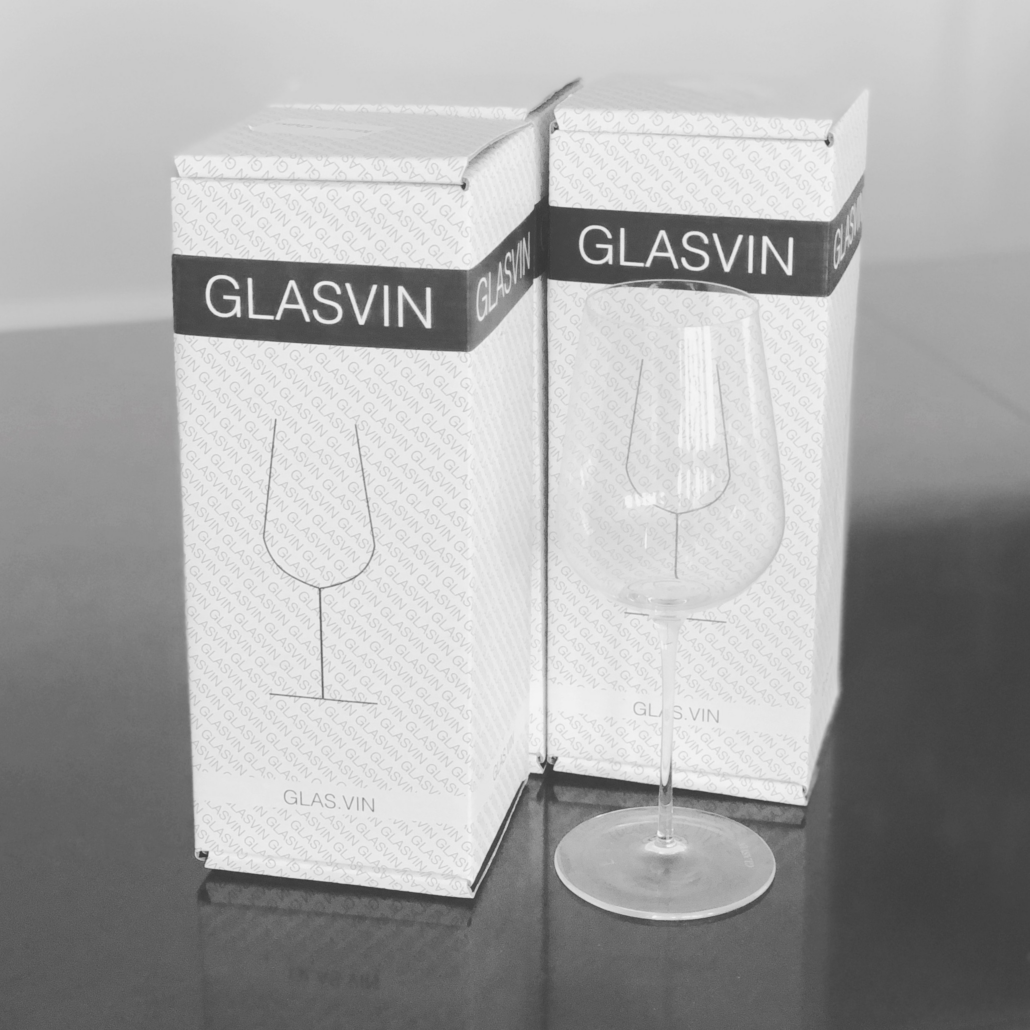

Value Creation and Marketing:
- David emphasizes creating value for customers through product quality and pricing.
- Packaging and branding were initially less polished but did not hinder sales due to the product’s perceived value.
- David Kong’s primary focus was on enhancing the drinking experience, making wine taste better with thinner glasses.
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Model:
- Glasvin sells primarily through its own website powered by Shopify.
- The decision was made not to sell on Amazon due to potential mismatches with the target customer base.
- Inbound sales, driven by word-of-mouth referrals and brand reputation, are a significant aspect of Glasvinl’s sales strategy.
Restaurant Sales:
- Glasvinl targets restaurants as a marketing channel, gaining exposure and credibility through partnerships with prestigious events like La Paulée.
- The company provides glasses for rental at events, leveraging its association with high-profile wineries and events to expand its reach.
Evolution of Business Opportunities:
- Participation in La Paulée led to the development of a rental program for the glasses, diversifying revenue streams beyond direct sales.
- David identifies market gaps and opportunities, such as the demand for alternatives to Zalto glasses, and offers tailored solutions to meet customer needs.
Future Growth:
- Despite current success, David emphasizes the importance of continuous adaptation and improvement to drive future growth.
- The pursuit of growth involves remaining competitive, evolving the business model, and meeting evolving customer demands.