52. Mark Schaefer: The Future of Marketing Is Austrian – How Human-Centered Marketing Can Fix A Business Function That Has Lost Its Way.
This week I spoke with Mark Schaefer about his iconoclastic and deeply insightful book Marketing Rebellion, in which he expounds the solution to modern marketing’s failures, via an approach he calls Human-Centered Marketing.
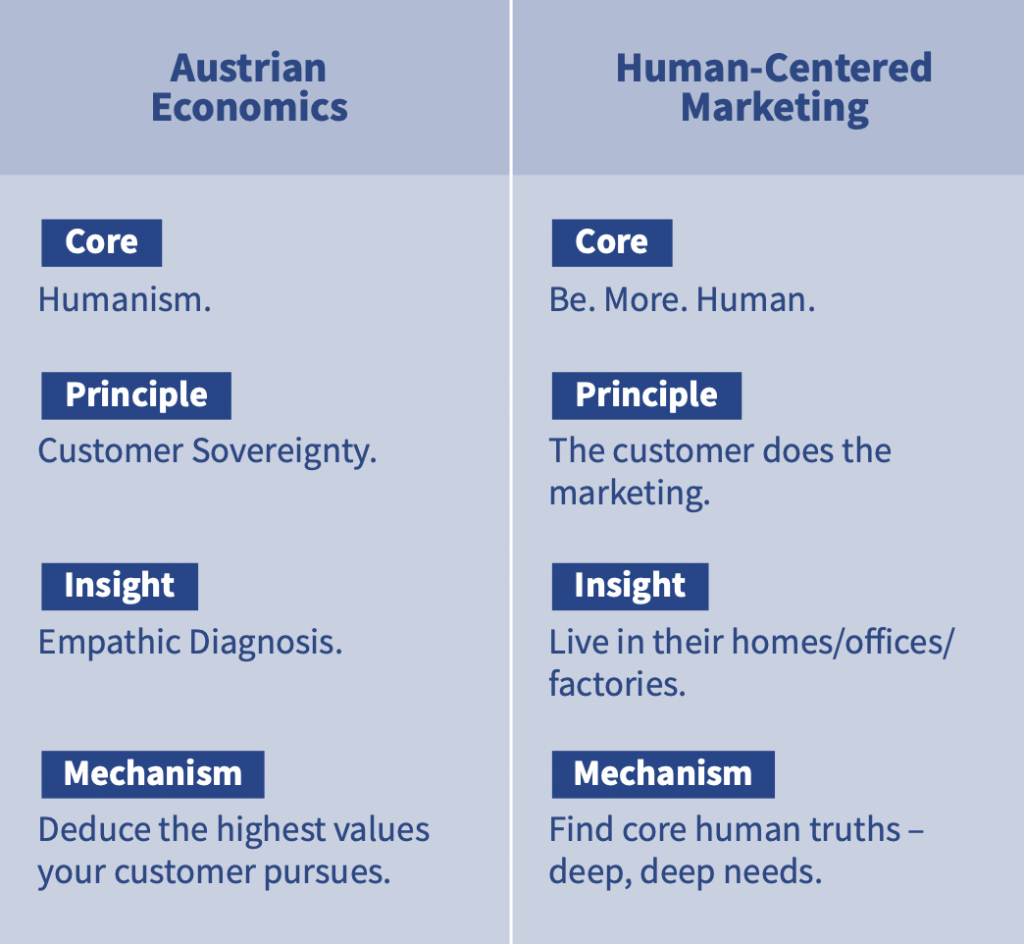
Listeners to Economics For Entrepreneurs and aficionados of Austrian Economics will recognize the close overlap between Austrian Economics and Human-Centered Marketing.
Key Takeaways & Actionable Insights
Marketing has lost its way – in its current state, it’s no longer a useful business growth tool for entrepreneurs.
- An obsession with technology has eclipsed the focus on people and human values.
- A mania for measurement has obscured emotional connections with customers.
- “Marketers hide behind their dashboards” and are not conducting conversations with customers.
The solution, says Mark Schaefer, lies in the principles of Human-Centered Marketing. Austrians can easily recognize these principles as our own.
The customer-sovereignty perspective yields actionable truths.
- Customers don’t need ads – they don’t see them, they don’t hear them, they block them.
- Customers are rebelling against the interrupt-and-annoy approach of marketers.
- The customer is in charge.
What do customers want from marketers? The answer for Mark Schaefer lies in Core Human Truths – what Austrians call Highest Values.
- They want to feel loved.
- They want to be respected
- They want to belong
- They want you to advance their self-interest
- They want proof that a firm or brand is contributing to their community
These are deep human needs that don’t change. Whatever the speed of change in market, these values are constant. Humanism lets marketers hold on to what is not changing, rather than being overwhelmed by change.
Marketing mantras like “loyalty” and “engagement” are false.
- Customers don’t want to be loyal; they want freedom and choice – they like shopping around.
- Engagement does not result from clicking on an e-mail and downloading a white paper or a coupon.
- These are dashboard measurements, not human values.
Mark’s recommendations are grounded in humanism.
Customers respond to shared meaning and shared values – so long as the sharing is authentic. Businesses must be loyal to consumers, never let them down, always be consistent. Live on their island.
Seek trust. Marketers have burned through trust. The Edelman Trust Barometer shows trust in business and brands and advertising going down for 11 straight years. Now brands must transcend the public’s mistrust.
Flip your branding. A brand is not what you tell customers. A brand today is what customers say about you to their friends and peers. People trust other people.
Let customers create their own value. This is pure Austrian Economics: customer value is an experience that takes place entirely in their domain. Brands and businesses facilitate – but can’t create – the customer’s value experience. Customers hire your brand or business or product or service to help them create value.
Marketing is promise management.
- Choose the promise you make to customers carefully – is it one they really want from you and will they trust you when you make it?
- Ensure that you have the capabilities to deliver on the promise. Don’t over-promise.
- Keep your promise every time, with no exceptions ever.
BONUS: Small and medium businesses have an advantage in human-centered marketing.
The larger the business, the harder it is to connect to customers on an individual, emotional level. Small business has an advantage in showing its face, demonstrating its personality and exhibiting trustworthiness.
Items Mentioned In This Episode
Mark Schaefer’s Human-Centered Marketing Manifesto is here.
For comparison, our Menger’s Manifesto, from Principles Of Economics, is here.
Find Mark’s book, Marketing Rebellion, here.
Mark’s website is https://businessesgrow.com
Free Downloads & Extras
Accounting From An Austrian (Misesian) Perspective: Our Free E4E Knowledge Graphic
Understanding The Mind of The Customer: Our Free E-Book
Start Your Own Entrepreneurial Journey
Ready to put Austrian Economics knowledge from the podcast to work for your business? Start your own entrepreneurial journey.