Digitally Enabled Harmony: The Organizational Model For The Post-Management World.
There is a deepening appreciation of the business firm as a complex evolving system (CES). The behavior of such systems can be understood through the lens of universal laws that have been discovered over the past 75 years or so of systems science studies. The findings of these studies point in a very different direction for the optimization of performance of firms than the traditional processes and methods of direction and control that fall under the heading of contemporary business management.
The mental model to replace management direction and control is harmonization – the unburdened harmony both of the firm interacting with its external environment (markets, customers, suppliers) and harmony within the firm between producer teams. The harmonizing catalyst is value – creating value for customers, and value and meaning in work for employees. Value acts as a coalescing unity (it’s what brings the firm and its markets into alignment) and provides a congruent shared meaning (everyone in the firm is devoted to value creation for others, and customers, partners and suppliers are collaborators in this purpose).
In the language of systems, value is the governing constraint. Constraints are a favorable influence on systems, shaping their development in the direction of collaboration, co-ordination and coherence. Constraints can be norms or cultural guidelines, or feedback loops, or conceptual frameworks, or even standards or processes, that lower barriers to value creation. Constraints bring about effects by channeling and facilitating value flow. They are the conceptual opposite of management structures and command and control philosophies: they are freeing rather than restricting.
The right governing constraints result in harmony, the productive emergence of (1) collective shared meaning (cognitive and emotional harmony) and (2) collaborative unity (behavioral harmony). This harmony unites both the internal and external environment: customers, suppliers and partners are as aligned as are internal functions.
The organizational unit for the harmony model is the team. Teams are deployed to develop solutions to problems that an individual can’t achieve. The members have multiple, complementary skills and a common task or goal. They collaborate to discover how best to work together for the common goal. They can exist within an assemblage of teams – teams of teams- embedded within the larger context of a firm or a corporation, and they are self-organizing in that context. The firm provides the governing constraint of shared intent and shared norms, while the teams operate in a bottom-up mode to affect the whole firm and improve system performance.
Harmonized teams
Teams develop a capacity to act as a network of people, things and narrative (shared meaning). They are characterized by fluidity of interaction and exchange. Individuals on a team are interdependent, and multiple teams can be interdependent with each other in the team of teams. Interdependency can cross boundaries (e.g. the marketing team might embrace both finance and operations) and between levels (e.g. combining planning and execution) because it is the quality of interactions that matter, not the structural arrangement of resources.
The Data Layer
The critical resource for teams to achieve high quality interaction is data from the environment. When information is rich and free-flowing, the quality of team interactions is increased; knowledge gaps are rapidly closed and feedback loops enable error correction and adaptation. In systems theory, higher team performance resulting from the flow of data is termed The Law Of Increasing Functional Information (LIFI).
In the context of firms needing to achieve competitively superior delivery of value to customers, they are called upon to continually improve their value function. To do so, they gather and process functional information – the data that tells them how to create value, how well they are creating value at present, and how to improve value delivery in the future. The more functional information they can collect and flow through the company, and the better they can process it, the higher their value creation performance. There is a selection process at work: the market selects those firms and value propositions that are most functional – most valuable – for them.
Digitally enabled harmonization
A new organizational model has emerged to make harmony the catalyst for firm-level performance: digital enablement. It has the following components:
- A direct connection to the external environment – to customers, partners, suppliers. This is the key transformational influence: the direct connection to customers and markets is the factor that has unleashed new business models such as those of amazon, AirBnB, Netflix and many of the exponential growth businesses of today.
- A data layer to collect and organize the inflow, applying A.I. and machine learning to identify patterns and insights, before human factors are applied. By routing data through the data layer and associated analytical software and models, insights can emerge spontaneously before the application of human judgment.
- An unstructured assemblage of functions that utilize the insights from the data layer to elevate value creation in their own domain: operations, commerce, service delivery, customer relationships and engagement, marketing and brand building. The functions develop a collective intelligence that increases the value performance of every project, team and individual.
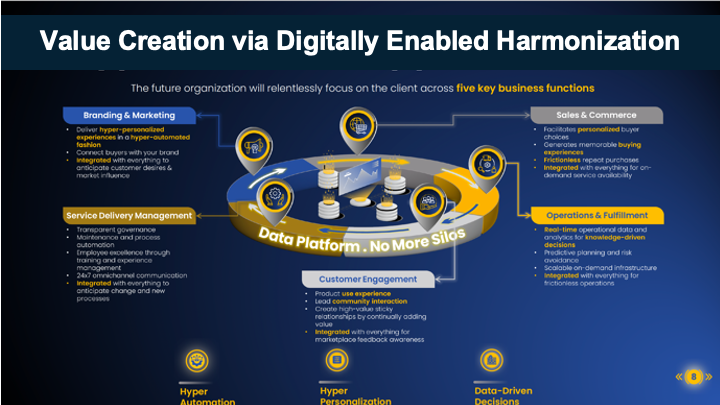
The core components of digitally enabled harmonization are:
- Philosophy: all good businesses start from sound philosophy. Digital harmonization is founded on a philosophy of value, nurtured by customer information, and enabled by the direct connection from customer to firm, without intervening barriers or distorting judgment.
- Information flow: in information theory, more data, processed more quickly and analytically, can drive value, so long as noise and equivocation are eliminated or reduced. The direct digital connection to the market supplies the flow and the A.I. and M/L processing provide the clarity of insights. Speed of response is important but not primary: clarity is the key.
- Self-organization: teams self-organize by identifying entrepreneurial goals for pursuing new customer value, combining knowledge, skills, resources and tools. The science of self-managed teams in the pursuit of customer value goals has become well-developed in agile software development, and the principles are fully transferable across all functions and projects. No central control is required, and improved results stem from the bottom up, rather than from top-down strategies or planning. The higher-level intent of the firm is realized through lower-level initiatives.
- Value: the primary governing constraint is value, the experience of greater well-being. This is what customers seek, so value creation by the firm generates the positive feedback loop – through the data layer – of revenue and profit as well as customer satisfaction and loyalty. It’s also what employees, associates and partners seek: meaningful work, creating value for customers.
- Generative culture: the critical human-in-the-loop component is active in functions at the team level, where creativity and imagination harnessed to insights generate new initiatives and implementations for testing and expanding in the marketplace. Performance-oriented teams are motivated and united by shared meaning and enjoy the collaborative participation in the pursuit of new customer value, and the collective learning via the active feedback loop. Interoperability across teams and across functions further strengthens the generative collaboration.
References
Alicia Juarrero: Context Changes Everything: How Constraints Create Coherence; MIT Press, 2023.
Johan Ivari, Annette Nolan: Team Up For Success: Harnessing Participatory Sense Making; Swedish Defence University, 2024.
Cooperative Consulting: Digital Enablement: Helping growth-minded clients accelerate into the Automated Economy, 2024
